ZINC STRONG
Based on 7 reviews
1 capsule per day with a glass of water. For adults only.
The benefits
-
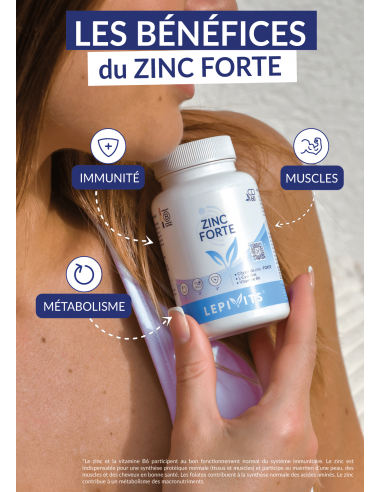
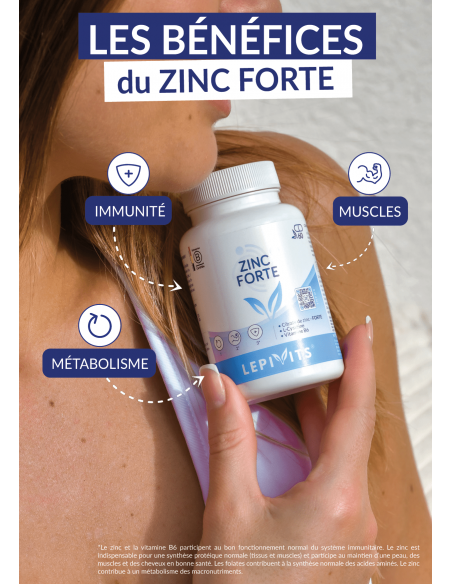
 Immunity
Zinc and vitamin B6 contribute to the normal functioning of the immune system.
Immunity
Zinc and vitamin B6 contribute to the normal functioning of the immune system.
-
 Muscles
Zinc is essential for normal protein synthesis (tissues and muscles) and helps maintain healthy skin, muscles and hair.
Muscles
Zinc is essential for normal protein synthesis (tissues and muscles) and helps maintain healthy skin, muscles and hair.
-
 Métabolism
Zinc contributes to the metabolism of macronutrients.
Métabolism
Zinc contributes to the metabolism of macronutrients.
Customer reviews
-
Le Zinc m’est indispensable !
-
Le Zinc Forte est très efficace je le recommande fortement !
Product qualities
-
 Pullulan capsule (100% vegetable)
Pullulan capsule (100% vegetable)
-
 Casein-free, gluten-free, lactose-free
Casein-free, gluten-free, lactose-free
-
 No preservatives, no pesticides, no artificial colours or flavours
No preservatives, no pesticides, no artificial colours or flavours
-
 Vegan
Vegan
-
 Recycling
Recycling
Nutritional information
| NUTRITIONAL INFORMATION | 1 CAPSULE | AR%* |
|
L-Cysteine Zinc element Vitamin B6 |
150mg 22,5mg 6mg |
- 225 428 |
*RI reference input.
This product cleverly combines zinc citrate, L-Cysteine, and vitamin B6, three key ingredients that play a role in promoting overall health.
Zinc citrate is a form of zinc derived from citric acid, known for its high bioavailability.[1] This means the body can easily absorb and utilize zinc, an essential mineral that contributes to the proper functioning of the immune system. L-Cysteine, an amino acid, works in synergy with zinc to promote better mineral absorption, thereby optimizing its effectiveness.[2] Lastly, vitamin B6 is used to enhance the effect of zinc.[3] This essential vitamin contributes to numerous metabolic reactions in the body, including the normal functioning of the immune system.
Technical Advantages of Zinc Forte
- High Bioavailability of Zinc Citrate: Zinc citrate is chosen for its high bioavailability, meaning the body can absorb it more efficiently than other forms of zinc. This form of zinc is derived from citric acid, a natural component found in fruits and vegetables, making the product more natural and easily usable by the body. This characteristic allows zinc to fully play its role in various essential biological processes.
- Optimization of Absorption by L-Cysteine: The presence of L-Cysteine, an essential amino acid, increases the absorption of zinc. L-Cysteine, an amino acid naturally present in many protein-rich foods, plays a crucial role in the transport of zinc, an essential mineral, through cell membranes.[7] This capability ensures that zinc is efficiently delivered to areas where it is indispensable for many biological functions, including tissue repair, immune function, and protein synthesis. This optimization of absorption ensures that the zinc doses provided are effectively used by the body to support its vital functions.
- Increased Effectiveness by Vitamin B6: Vitamin B6 plays an essential role in enhancing the effectiveness of zinc. It helps catalyze the reaction of zinc with other substances in the body, thus facilitating its role in the immune system and in protein metabolism. Vitamin B6 is also vital for the synthesis of neurotransmitters, adding an additional layer of benefits to the Zinc Forte formula.
- Formulation Without Synthetic Fillers: Our commitment to purity extends to the absence of fillers, binders, or diluents, often used in dietary supplements to reduce production costs. Zinc Forte contains only what is necessary to deliver its effects, without unnecessary fillers, ensuring that each component serves a nutritional or functional purpose.
- Conditionnement
- 60 vegetarian capsules
- Composition
- L-Cysteine hydrochloride, capsule shell: pullulan, zinc citrate, rice starch, vitamin B6 (pyridoxal 5'-phosphate).
- Main indication
- Sport - Tonus
- Specific indication
- Immune defences
- Dosage
- 1 capsule per day with a glass of water. For adults only.
- Recommandations
- Food supplement, cannot replace a varied and balanced diet. To be taken as part of a healthy lifestyle. Inform your doctor or pharmacist if you are taking medication at the same time. Keep out of the reach of children. Store in a cool, dry place. Do not exceed the indicated dosage.
- Notification number
- PL 3760/21
- Posologie (nbr gélules/jour)
- Condition
- New product
- ean13
- 5430002936666